CO2還元によるHCHO合成に関する華中科技大学との共同研究の成果がApplied Catalysis B誌 (Elsevier)にAcceptされました。Our collaboration with Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Applied Catalysis B (Elsevier).
「Catalytic aqueous CO2 reduction to formaldehyde at Ru surface on hydroxyl-groups-rich LDH under mild conditions」
Deng, Lidan; Wang, Zheng; Jiang, Xingmao; Xu, Jie; Zhou, Zijian; Li, Xiaozhong; You, Zhixiong; Ding, Mingyue, Shishido, Tetsuya; Liu, Xiaowei; Xu, Minghou
Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2023, 322, 122134. DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122124
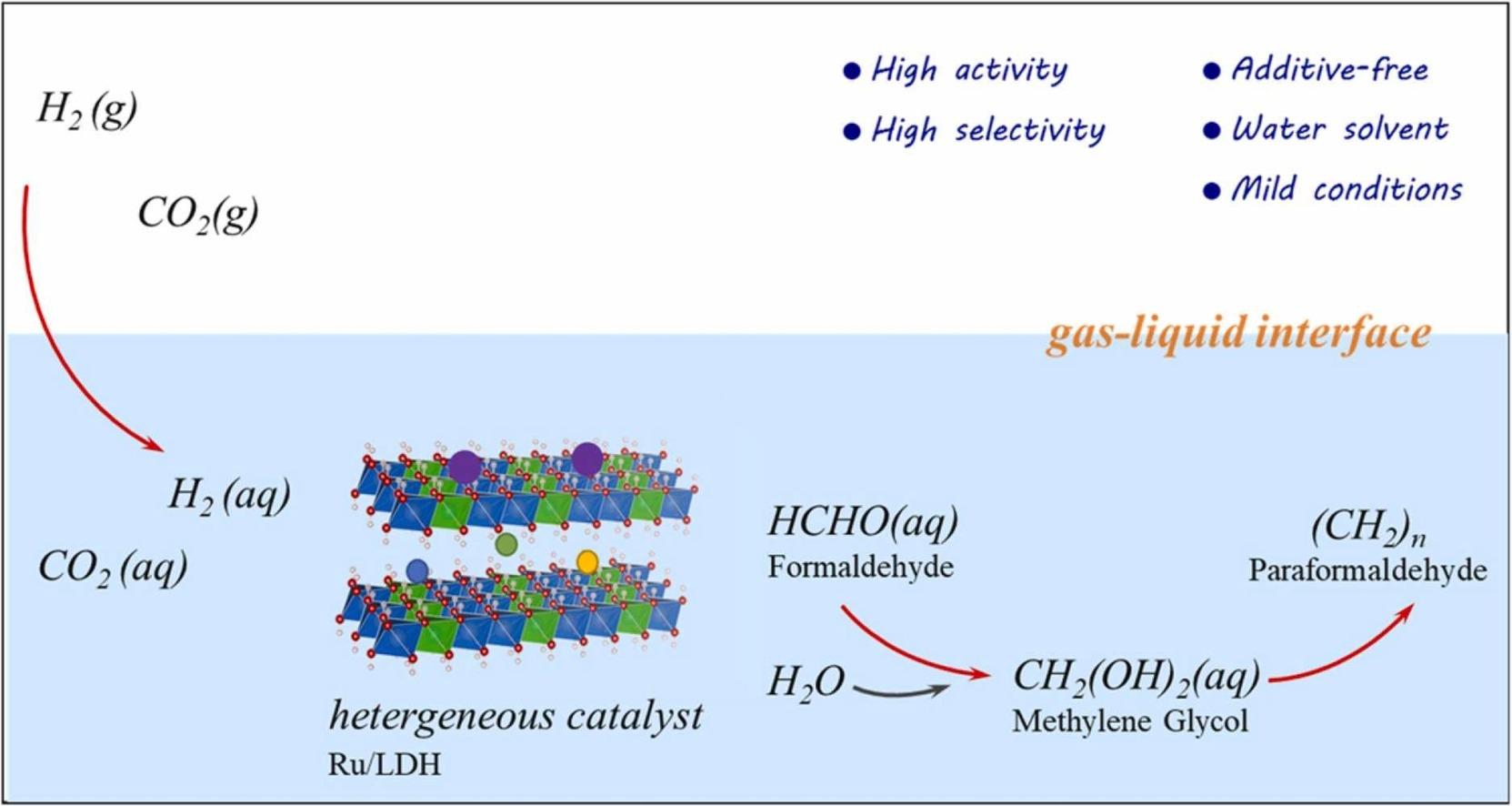
Various value-added chemicals such as formic acid, carbon monoxide, methane, methanol, have been obtained using CO2 as a feedstock. However, formaldehyde generation from CO2 is less reported. Here, we performed CO2 hydrogenation with H2 in additive-free water and used layered double hydroxide supported Ru as the heterogeneous catalyst. It was found that gaseous CO2 and H2 could be efficiently and selectively converted to formaldehyde dissolved in water even at room temperature with ambient pressure. The highest gaseous CO2 conversion of 89.7% and a formaldehyde yield of 58.7% were achieved using a Ru/LDH-red catalyst in water at 30 °C with 10 bar CO2 and 10 bar H2. Combined with experimental and theoretical studies, HCOOH was found as the important reaction intermediate. The rich surface -OH of LDH and hybrid electronic state of Ru over Ru/LDH-red catalyst resulted in highly efficient HCHO formation. Our findings offer opportunities to one energy-efficient formaldehyde synthesis method.