メタン活性化に関する九州大学、産総研、北九州市立大との共同研究の成果がJournal of the Japan Petroleum Institute誌 (JRI)にAcceptされました。Our collaboration with Kyusyu Univ. AIST, and Kitakyusyu City Univ. in Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute (JRI).
「Particle Size Effect on Hydrogen Cyanide Synthesis with CH4 and NO over an Alumina-supported Platinum Catalyst」
Tatsuya YAMASAKI, Atsushi TAKAGAK, Tetsuya SHISHIDO, Kyoko K. BANDO, Tetsuya KODAIRA, Junichi MURAKAMI, Jun Tae SONG†, Eiki NIWA, Motonori WATANABE, and Tatsumi ISHIHARA
Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 2022, 65, 184-191. DOI: 10.1627/jpi.65.184
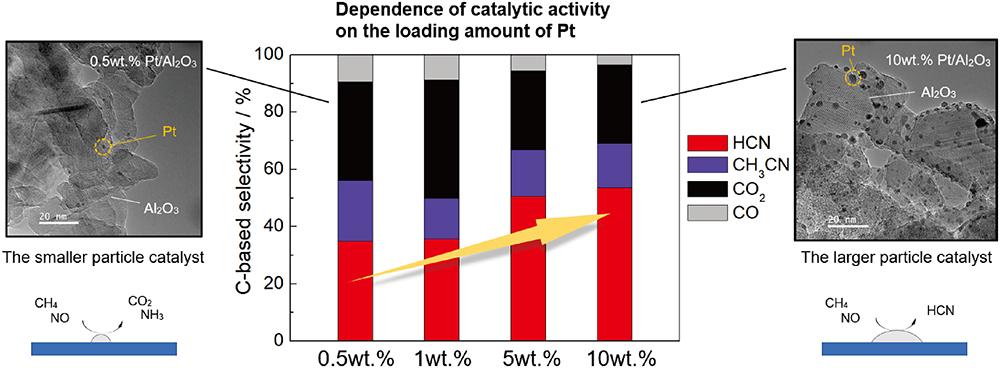
The particle size effect of platinum nanoparticles on the conversion of methane (CH4) into hydrogen cyanide (HCN) using nitric oxide (NO) as an oxidant over the Pt supported (γ+θ)-alumina was investigated. The Pt catalysts with various average particle size in the range of 1.6 to 4.1 nm were obtained by controlling the loading amount and calcination temperature. Amount of the Pt surface sites was determined by CO titration using a pulse method and the catalytic activity was evaluated under same contact time. In case of the catalysts having small particle size (1.6-3.2 nm) of Pt, NO conversion was lower than the large one. The catalysts having large particle size (4.1-4.2 nm) exhibited high selectivity of HCN reaching 53.5 % at 1.3 % C-based yield at 400 °C over 10 wt% Pt/Al2O3. One of the reasons for higher activity with the larger Pt particles is suppression of the sequential reaction of HCN to carbon dioxide and ammonia which likely proceeded at the interface between metal and support. Pt L3-edge X-ray adsorption fine structure (XAFS) spectra showed that the small particle catalysts were covered with Pt_CN species after the reaction test. In contrast, Pt_CO was observed as main adsorbed species on the large particle catalysts, suggesting that HCN desorption process was facile for the larger Pt particle case.