Feng Shixiang君が中心となり行った理学研究科の波田雅彦先生らとの共同研究の成果がACS Catalysis誌(ACS)にAcceptされました。Our paper reporting selective oxidation of glycerol over supported PtBi catalyst was published in ACS Catalysis (ACS).
「Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of the Role of Bismuth in Promoting the Selective Oxidation of Glycerol over Supported PtBi Catalyst under Mild Conditions」Feng, Shixiang; Yi, Jun; Miura, Hiroki; Nakatani, Naoki; Hada, Masahiko; Shishido, Tetsuya
ACS Catalysis, 2020, . DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c00974
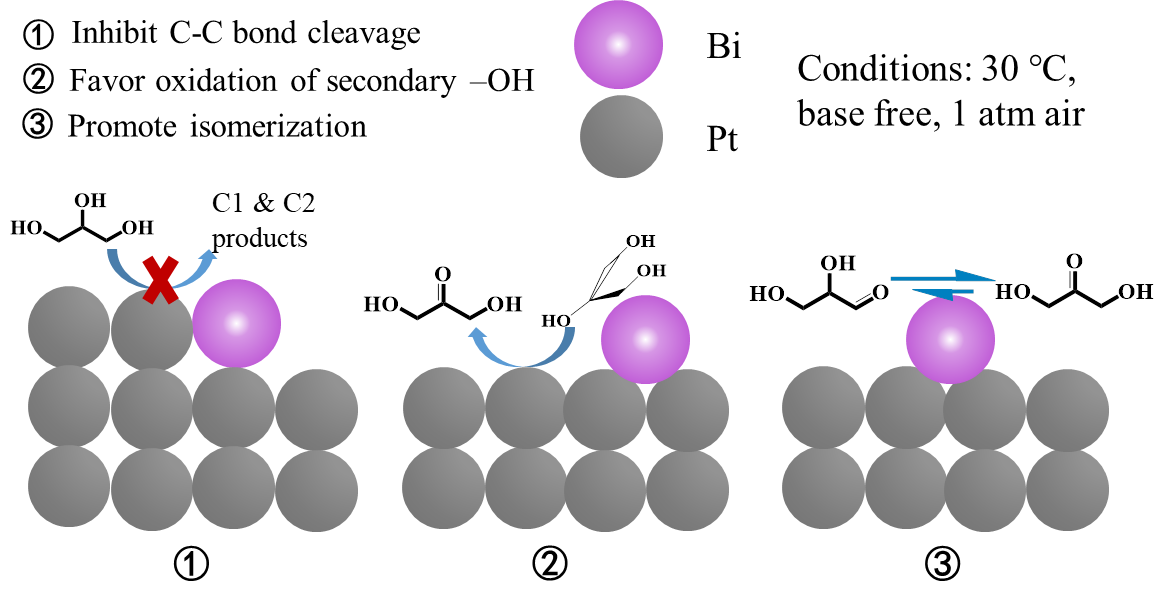
Supported palladium-gold alloy-catalyzed cross-coupling of aryl chlorides and hydrosilanes enabled the selective formation of aryl-silicon bonds. Whereas a monometallic palladium catalyst predominantly promoted the hydrodechlorination of aryl chlorides and gold nanoparticles showed no catalytic activity, gold-rich palladium-gold alloy nanoparticles efficiently catalyzed the title reaction to give arylsilanes with high selectivity. A wide array of aryl chlorides and hydrosilanes participated in the heterogeneously-catalyzed reaction to furnish the corresponding arylsilanes in 34-80% yields. A detailed mechanistic investigation revealed that palladium and gold atoms on the surface of alloy nanoparticles independently functioned as active sites for the formation of aryl nucleophiles and silyl electrophiles, respectively, which indicates that palladium and gold atoms on Catalytic biomass conversion under moderate reaction conditions is of great significance as a means of developing synthesis routes to replace petroleum products. The present study demonstrates that a high glycerol conversion (40.9%) and significant dihydroxyacetone (DHA) selectivity (65.1%) can be obtained at 303 K under 1 atm air in a base-free solution during the oxidation of glycerol over a bimetallic catalyst supported on SBA-15 (Pt-Bi/SBA-15). CO chemisorption data and transmission electron microscopy characterization show that Bi was deposited on both the step and terrace sites of the Pt surface and consequently modified the catalytic activity. Kinetic studies revealed that the addition of Bi significantly altered the reaction route such that DHA was produced rather than glyceraldehyde (GLD) during the initial stage of the process. 13C NMR analysis found that glycerol tended to chelate with Bi atoms via hydroxyl groups (−OH) to modify the stereochemistry of the reactants. Density functional theory calculation confirmed that each of the three hydroxyl groups of glycerol were captured by the bismuth species, and the middle −OH simultaneously interacted with the platinum surface resulting in selective oxidation of glycerol to DHA. Bismuth ions (Bi3+) were also determined to promote the isomerization of GLD to DHA, which improved the DHA selectivity. These experimental and theoretical results together explain the high activity of the Pt-Bi/SBA-15 under moderate conditions.alloy nanoparticles work together to enable the selective formation of aryl-silicon bonds.