Deng Lidan君、大久保智世君がが中心となって行ったPt-Sn合金触媒によるn-ブタン脱水素に関する研究成果がCatalysis Science & Technology (RSC)にAcceptされました。Our paper reporting dehydrogenation of n-butane by supported Pt-Sn alloy catalysts was accepted in Catalysis Science & Technology (RSC).
[Featured on a journal cover]
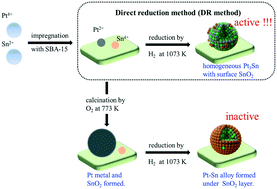
「The importance of direct reduction in the synthesis of highly active Pt-Sn/SBA-15 for n-butane dehydrogenation」.
Deng, Lidan; Miura, Hiroki; Ohkubo, Tomoyo; Shishido, Tetsuya; Wang, Zheng; Hosokawa, Saburo; Teramura, Kentaro; Tanaka, Tsunehiro
Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9, 947 - 956. DOI:10.1039/C8CY02173B
Supported Pt-Sn bimetallic catalysts directly reduced by H2 (DR method) are highly active for the dehydrogenation of n- butane, while the catalysts calcined in air, followed by H2 reduction (CR method), were totally inactive regardless of calcination temperature and Sn/Pt ratio. The present work investigated the detailed bulk and surface structural properties of the catalysts with various characterization techniques. The results suggest that both DR and CR methods led to the formation of bulk Pt-Sn alloys (e.g. Pt3Sn,PtSn). However, calcination before reduction significantly changed the catalyst surface properties. The SnO2 layer were located on the surface of Pt-Sn alloys and/or Pt nanoparticles when the catalysts prepared with CR method. In contrast, the DR method induced more surface exposed Pt atom from Pt3Sn alloy, which plays an important role in the superior catalytic behaviors for n-butane dehydrogenation.